Book Your Appointment
Common Allergic Diseases
Allergic Rhinitis (सायनस) :
Allergic Rhinitis is an inflammatory condition of the nasal mucosa characterized by sneezing, watery nasal discharge and obstruction of nasal passages. It may be associated with conjunctional and pharyngeal itching, lacrimation and sinusitis. Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis is commonly caused by exposure to allergens such as pollens, especially from grasses, trees, weeds, and molds. Perennial Allergic Rhinitis is frequently due foods house dust and animal dander.
Nasal mucosal surface probably allows penetration of allergens deeper into the nasal mucosa of a sensitized individual results in IgE – dependent triggering of mast cells. Subsequently the mediators that cause mucosal hyperemia, swelling and fluid transudation are released. Inflammation sets in tissue-cells where allergens make contact with mast cells. Obstruction of openings of sinuses may result in development of secondary sinusitis with or without bacterial infection.
Diagnosis :
- Accurate history of symptoms may correlate with time of pollination of plants in a given locale.
- Special attention must be paid to other potentially sensitizing antigens such as pets.
- Physical examination; nasal mucosa may be boggy or erythematous; nasal polyps may be present; sinuses may demonstrate decreased transillumilation; conjunctiva may be inflamed and edematous manifestations of other allergic conditions (eg Asthma, Eczema) may be present.
- Skin tests to inhalant and/or food antigens.
- Nasal smear may reveal large number of Eosinophil, presence of neutrophils may suggest infection.
- Total and specific serum IgE (As assessed by immunoassay) may be elevated.
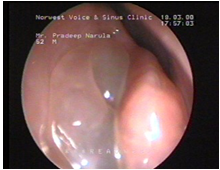
Nasal Polyps

A patient of allergic rhinits
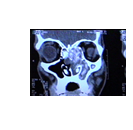
X-rays of Nasal polyps
X-rays of Nasal polyps
Differential diagnosis :
Vasomotor Rhinitis, Upper Respiratory Infections, Irritant exposure, pregnancy with nasal mucosal edema, rhinitis due to use of beta adrenergic agents are some the common diseases confusing with Allergic Rhinitis.
Prevention: Identification and avoidance of offending antigen.
Treatment :
It can be divided in two parts
1. Specific –This management consists of identification of specific offending agents and prevention. Our statistics has been shown elsewhere.
2. Symptomatic-This is centered around blocking the effects of allergic reactions with pharmaceutical agents.
a) Antihistamines: Chlorpheniramine maleate 12 mg orally twice a day
Terfenadine 60mg orally twice a day
Astemezole 10 mg orally four times a day
Loratadine 10 mg orally four times a day
There are many more in the market.
Note: Life threatening cardiac arrhythmias have occurred due to inhibition of the metabolism of Terfenadine or Astemizole by concomitantly administrated microlide antibiotics (such as Erythromycin and Chlarithromycin) or broad spectrum antifungal agents such as Ketoconazole or Itraconazole.
The use of either Tarfenadine or Asteminazole is contraindicated in combination with these drugs; and in individuals with concomitant medical illness that impairs hepatic function or predisposes to cardiac arrhythmias.
- Oral symphathomimetics eg pseudophedrine 30-60 mg orally four times a day; may aggravate blood pressure and produce increase in heart rate. The combination antihistaminic and decongestant preparations may balance side effects and provide expected patient’s relief in symptoms.
- Tropical vasoconstrictors these should be used sparingly due to rebound congestion and chronic rhinitis associated with prolong use.
- Topical nasal steroids eg beclomethasone 2 sprays in each nostril twice or thrice a day.
- Topical nasal Cromolyn Sodium 1-2 sprays in each nostril four times a day.
- Hyposensitization therapy: If more conservative therapy is unsuccessful then this complex and prolonged therapy will be opted for. You can find more detailed information in the general information section.
Bronchial Asthma (दमा/अस्थमा) :
Etiology = It is an inherited disease (Genetic) where environmental factors have an important role.
- Allergic Asthma is associated with Rhinitis, Urticaria, Eczema, increased IgE and +ve reaction to intradermal antigens.
- Some patients have non Atopic Asthma (no H/O allergy) or idiosyncratic asthma. Asthma in early life usually has allergic basis.
- Asthma occurring in later life usually has no history of allergy
Pathogenesis :
The repeated exposure of allergens sensitizes the mucosal mast cells , eosinophilic cells and lymphocytes. Due to cellular events a large number of inflammatory mediators are liberated. IgE is mainly involved in these events. Thus a complex chain of events takes place and three changes occur in the tracheo-bronchial wall. First, there is spasm of the wall muscles. Second there is inflammation in the wall leading to cell accumulation and fluid pouring. Third, there is mucus impaction in the lumen of respiratory tract. All these changes lead to increased resistance to air flow and result in the symptoms seen in Bronchial Asthma.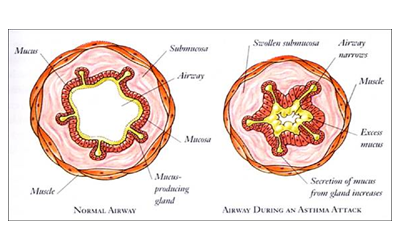
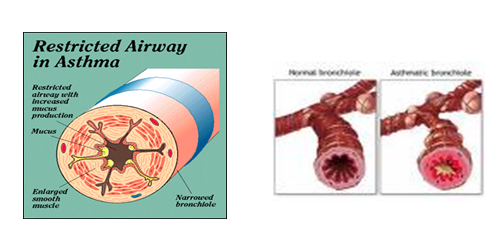
Clinical features :
- There is a triad of shortness of breath, cough and wheezing. The respiratory rate increases, sense of constriction in chest, productive or non productive cough, wheezing in inspiration and expiration, prolonged expiration, The heart rate rises and some times there may be some systolic hypertension. AP diameter of the chest increased.
- Wheezing is high – pitched and there is loss of any sounds in severe cases.
- Accessory muscles become active.
- There is paradoxical pulse due to large negative intra thoracic pressure.
- As the disease progress there are deleterious effects on the lungs. They become more distended; there can be damage of lung parenchyma. Vasculature in the lung parenchyma can have increase in pressure. At the sever stages of Asthma right side of heart gets affected and failure may ensue.
- As this disease is prolonged morbidity there are many psychological.
Complications :
- Atelectasis: this means shrinkage of a part of a lung. This is due to blocked bronchi.
- Spontaneous Pneumothorax : When air leaks in the pleural space it is called as Pneumothorax. Here patient’s symptoms worsen and shortness of breath becomes very sever.
- >Pneumomediastinum: When the air goes in the midline portion of the chest it is called as pneumomediastinum.
- Respiratory failure: Due to many conditions of lungs they may not be able to maintain the Oxygen levels of blood and there may be retention of CO2. This stage is called respiratory failure. Right heart failure: As mentioned above this a sequel of prolonged sever asthma
Diagnosis :
The clinical picture is almost diagnostic; but investigations are needed to rule out other diseases. Haemogram is done to assess the Eosinophilic cell count. There are serological investigations to assess IgE –specific antibodies as well. So there is no unequivocal opinion about this modalities; therefore we rarely recommend. Spirometry is a technique of estimating various lung volumes. Now a days computerized machines are available in our country. This modality will depend on the performance of the patient apart from the lung capacities. There fore one must understand exact maneuver to avoid exhaustion.Forced Vital Capacity (FVC) It the maximum volume of air that can be forcibly breathed out after maximum inspiration.
Forced Expired Volume in first second (FEV 1) This the volume of air exhaled out in first second while performing FVC.
Peak Expiratory Flow rate(PEFR) : This is the maximum speed of air flow while performing FVC.
In Bronchial Asthma FVC remains normal; but FEV1 is disproportionately reduced. Thus FEV1/FVC ratio decreases. Similarly PEFR also reduces. These changes are reversible spontaneously initially or with bronchodilators.
Allergy Testing: This is a very important investigation to diagnose the allergic cause of Bronchial Asthma. More details have been described in the general introduction of allergy.
Treatment :
A prolonged management plan has to be adopted by the patients. As previously stated this is a multifaceted disease; and multiple factors should identified and corrected. Then only a patient establishes equilibrium with the disease. We suggest following management plan:
A) Identification of allergens;
B) Prevention Of allergens: This is based on the identification of your troubling allergens. If you are fortunate, easy to avoid allergens will be the culprit. You can avoid them and get rid of asthma. We have seen that many a times only food avoidance can give you dramatic relief even though you may be sensitive to many other ones. Some times domestic allergens like fungi and house –dust –mites to can be easily controlled by appropriate measures. These have been described in details somewhere else.
C) Symptomatic management: This consists of commonly described medications. They give relief of symptoms. There fore there are large numbers of drugs available in market. Quick relief medications.
- Short acing β2 agonists.- These drugs have relatively short duration of action ranging from 4 to 6 hours.Therefore patients should not takr these medications too frequently.The examples are : Salbutomol, Albutomol, Orciprenaline. Fenoterole
- Long acting β 2 agonists. These drugs have longer duration of action : 12 to 18 hours. There fore frequency of these drugs can be less. The examples are : Formoterol, Salmeterol
- Methyl xanthines. These are oral preparations. Some of them are available as parenteral preparations as well ; and the examples are: Theophylline Aminophylline and doxiphylline
- Inhaled glucocorticoids. There are many such drugs available in market: beclomethasone dipropionate, budesonide, fluticasone propionate, mometasone, cyclosenide. Your physician knows best about these drugs. There are many advantages with inhaled preparations. Fewer doses are required, there fore fewer side effects. They reach directly to the site of action. Thus there is quick onset of action.
- Mast cell stabilizing agents. Sodium cromoglycate, Nedocromil, Ketotifen. These drugs should be taken preferably before the exposure of allergens.
- Leukotrine modifiers. These drugs act by modifying the mediator called leukotrine. Though they created high expectations there role is limited to add on therapy. Montelukast,Pranlukast,Zafirlukast are theexamples of this category.
Devices :
Now a days management of Bronchial Asthma involves devices of drug delivery. Frequently an Attack of Asthma is sever and patient may not be able to get medical help immediately. More over these drugs have to be given through parenteral routes. This all can be overcome with the help of inhalation devices for asthma. They are as follows:
Dry powdered Inhalers: In these devices a capsule containing active medication is punctured or opened mechanically and a specified dose can be inhaled. These are simpler devices; easy to use and effort dependant. A patient needs no training to use these devices.

Metered Dose Inhalers :
These devices use inert gases to suspend the active medication. The design of these devices is more complicated. The dose required here is less than above devices. Moreover they are less effort dependent. But these devices require training. All of the products have an information leaflet explaining use and relevant information. A patient is expected to read carefully.
Method of inhalation: The patient should in upright position and hold the device as shown in picture with his fingers. Hold the device in mouth with lips tight around it. Then he should exhale out all the air through nose; and start a deep inhalation. You must trigger the device in the early phase of inspiration. Then only the medication will mix with inhaled air and reach to your lungs. This is important otherwise medication will deposit in the pharynx. Then you must continue inhalation uninterrupted to full chest. Hold the breath for some time and then exhale.
Nabulisers :
These devices are useful in delivering the drugs in aerosol form. i.e. They prepare mixture of drug and vapor so that the drug can be delivered effortlessly to the lungs of even serious patients. Many varieties were introduced in the market. A mechanical one is based on principle of churning the watery solution of a medication and delivering through the tubes. Ultra sonic devices use the principle of high frequency
Use of nebulisers was fashionable in medical practitioners due to many advantages. It is effortless for a patient. Medications can be administered to even an unconscious patient. It also keeps respiratory tract well hydrated. There are some disadvantages also. Medication goes waste in expiratory phase. The results cannot be better in cooperative patients.
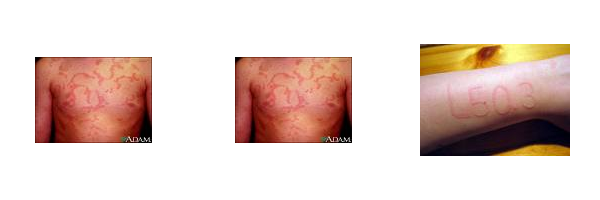
Definition = may occur together or separately. Urticaria involves superficial
Urticaria & Angioedema (स्किन एलजीं) :
Dermis and presents as circumscribed weals with raised surpinginous borders and blanched centers. Weals may coalesce. Angioedema involves deeper layers of skin and may include subcutaneous tissue. There disorders may be classified as.
- IGE dependent including Atopic, secondary to specific allergens and physical stimuli especially cold.
- Complement mediated ( including hereditary angioedema and hives related to serum sickness or vasculitis )
- Non immunologic due to direct mast cell releasing agents or drugs that influence mediator release and Idiopathic.
PATHO PHYSLOLOGY :
Characterized by massive edema formation in the dermis ( and subcutaneous tissue in angio edema ) presumably the edema is due to increased vasopermeability caused by mediator release from mast cells or other cell populations
Diagnosis :- History with special attention to possible offending exposures and /or ingestion . As well as the duration of lesions vasculitic urtecordia typically resists longest than 72h where as conventional Urticaria often has a duration of less than 48h.
Diagnosis:- History with special attention to possible offending exposure and or ingestion as well as
- Skin testing to food and/or inhalant antigens.
- Physical pronocation eg challenge with vibratory or cold stimuli.
- Laboratory examination = complement lenels, ESR ( neither an elenated ESR nor hypo complimentemia ) is observed in IGE – mediated Urticaria or angio edeme ); c1 esterase inhibitor lenels if history suggests hereditary angioedema; exyoglabulins, hepatitis B, antigen, and antibody studies, auto antibody serene.
- Sin biopsy may be necessary.
Differential diagnosis :- A topic dexmatitis, cutaneous mastocytosis ( Urticaria pigmentosa ), systemic mastocytosis.
Prevention :- Identification and avoidance of offending agents of possible.Rx treatment
- H1 and H2 antihistamines may be helpful eg ranitidine 150 mg Pobid; diphenhydramine 25-50 mg pogid; hydrolyzing 25-50 mg Pobid
- Cyprohepatadine 4 mg Pobid may be helpful.
- Sympthamimatic agents occasionally are useful.
- Topical glucocorticoida are of no value in the management of Urticaria and or angioedema. Because of their long term toxicity, systemic glucocorticoids should not be used in the treatment of idiopathic allergen- induced or physical Urticaria.
Ulcerative Colitis :
This disease has not been, so far, included in the list of allergic diseases by many standard medical books. However the basic pathoganesis is very much on the lines of immunological reactions. Reader is therefore advised to consider the rationality and discretion before drawing final conclusions.
Pathology = Colonic mucosal inflammation rectum almost always involved, with inflammation, rectum almost always involved with inflammation extending continuously ( no skip areas ) proximally sera variable extent, histological features include epithelial damage, inflammation, exypt abscesses, loss of goblet cells.
Clinical manifestations:- Bloody diarrhea, mucus, fever, abdominal pain, tenesmus, weight loss, spectrum of severity ( majority of cases axe mild )
Limited to recto sigmoid in severe cases dehydration, anemia, hypokalemia, hypoalbuminamia.
Complications :- Toxic megialon, colonic perforations cancer risk related to extent and duration of colitis, often preceded by or coincident with dysphasia ( neoplastic changes in individual epithelial cells ) which may detected on suxneillance colonoscopic biopsies.
Diagnosis = sigmoidoscopy colonoscopy, muscosal exytlema, granulality, fxiability exudates, haemorchage, ulcers, inflammatory polyps ( psudopolyps). Bariums enema, loss of haestorations mucosal irregularity ulcerations.
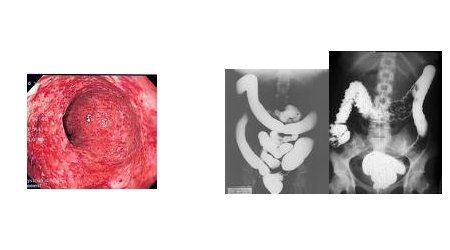
Treatment :
- Sulfasalazopyrine.
- Elsalazine.
- Mesalamine.
- Mesalamine ( pentasa )
- Cyclosporine.
Food Allergies :
Food allergy is still one of the most difficult of allergy problems.Many patients who believe they have chronic allergy to foods, do not have the food allergy. However they may have another medical problems such as
- Gasto interstinal enzyme deficiencies ( eg lactose intolerance)
- Reactions to chemicals in food ( eg tyramine, nitrites or casein)
- Psychosomatic problems
- Food intolerance ( eg peas and carrots syndrome seen in toddlers with rapid gastro intestinal transit time who get loose stools after ingestion of high fiber foods)

Pathophysiology :
The most important feature which distinguishes allergic ( Atopic) individuals is that following an allergic stimulation they develop sustained immunoglobulin – E ( IgE) antibody response to a particular allergen. A normal individual does not produce a high titer of IgE antibodies. Those antibodies become anchored to FC receptors on the surface of mast cells and basophiles. These cells liberate mediators only after re exposure of same antigen. Thus all the features of food reactions are due to release of active mediators and cellular participation. The allergic response occurs in genetically predisposed people
Clinical features:- Reactions due to IgE dependent sensitivity are
- Anaphylaxis.
- Urticaria and angioedema.
- Asthma
- Gastro intestinal problems.
- Atopic dermatitis diagnostic method of determining IgE – mediated food hyper sensitivity.
Established methods :
- Allergy skin test.
- Oral challenges ( open single or double blind)
- Elimination diet.
- RAST
Unproven technique :
- Cytotoxic test
- Provocation subcutaneous test
- Provocation sublingual test.
Anaphyloxis :
Definition = A life threatening systematic hypersensitivity reaction to content with an allergen, it may appear with in minutes of exposure to the offending substances manifestations include respiratory distress, pluxites, Urticaria, mucous membrane swelling, gastro intestinal disturbance including naurea and nomiting painand diarchea and vascular collapse. Virtually any allergen may invite an anaphylactic reaction but among the more common agents are oroteins, such as a antisera hormones pollen extract hymenoptera nunom leads drugs especially ( antibiotics ) and mastic agents. Atopy does not seem to redisplayed to anaphylaxis from pencillin or venom exposures.
Clinical presentation
Time to on set is variable but symptoms usually occurs with in seconds to minutes of exposures to the offending antigen.
- Respiratory mucous membrane swelling, hearse ness, strider wheezing.
- Cardiovascular: tachycardia, hypotension.
- Cetaceous: Pluralities , Urticaria, angieedema
Diagnosis = Made by obtaining history of exposure to offending substance with subsequent development of characteristic complex of signs and symptoms.
Treatment:- Mild symptoms such as pluralities and Urticaria can be controlled by administration of 0.2 to 0.5 ml of 1:1000 epinephrine solution SC repeated at 20 minutes intervals as necessary.
Anl. V infusion should be initiated. Hypotension should be treated by 1.v administration of 2.5 ml of 1:50,000 epinephrine solution at 5 to 10 min intervals, volume expanders e.g., as normal saline and wasopressor agents e.g., dopamine, if intractable hypotension occurs.
Epinephrine provides both alpha-and beta adrenergic effects resulting in were construction and bronchia’s smooth muscle relaxation. Beta blockers are relatively contraindicated in persons at risk for anaphylactic reactions .
The following should also be used as necessary.
- Antihistamines 50 to 80 mg l.m
- Diphenhydramine 0.25 to 0.5 gm l.v for bronchospasm.
- Oxygen
- Glucocorticoids – lv not useful for excute manifestations but may help control persistent hypotension or bronchospasm prevention = avoidance of offending antigen, where possible, skin testing and desensitization to matavoils such as penicillin and hymenoptera nenon if necessary.
Eczema :
The word eczema scans to have originated in AD 543 from the Greek word ekzin which means to boil or to ofter vesce . It is a type IV Delayed hypersensitivity reaction incompassing a broad range of conditions that begin as spongiotic dermatitis and may progress to uchenified stage . Clinically it may present as red edematous plague which may have grooslly visible small vesides suk – acute cessions have associated scales or crusting while long standing lesuis become lichenified severe pruritis is a pronivant accompanying synpton with intensity of itching increased by stress , heat and physical certion . Eczema may remain localized as in eae eczema , lychid dermatitis , nipple eczema , hand eczema ( major occupational dermatitis ) and eczema treatment regemain includes both pharmacological and supportive . superpotent and potent topical steroed agent along with occasional systemic cortico stored and anti – histoninics is the mainstay . Maintenance of proper health hygiene and identifications with protection from the allergen in very case must be inuesaged . Treatment regimen must be practical and should allow the patient to function as normally as be can .
The aetiology of Atopic dermatitis ( eczema ) is not known. However there may usually be a personal or family history of Atopic diseases. ( Hay fever, Asthma, Atopic Dermatitis) with a tendency of IgE mediated susceptibility disorders. Dry hyperirritable skin, food, allergens, and increased to bacterial, viral or fungal skin diseases may acts predisposing factors.
In adults the lesion appears as erythema and lichenified an any part but more so on the flexures of the body skin appear dry and thickened it is diagnosed an clinical grounds. Blood characteristically shows high level of IgE.
Treatment:- Avoidance of irritants, cutaneous hydration , topical glucocorticoids, treatment of infected lesions. Systemic glucocorticoids are used only for severe exacerbations unresponsiveness to topical conservative therapy.
Allergic Conjuctinitis :
Allergic conductivities, the most common form of eye allergy is a hypersensitivity reaction to specific airborne antigens ocular allergic manifestations Justas the disease has manifestations in various systems of the body, the eye may be involved in the following ways.
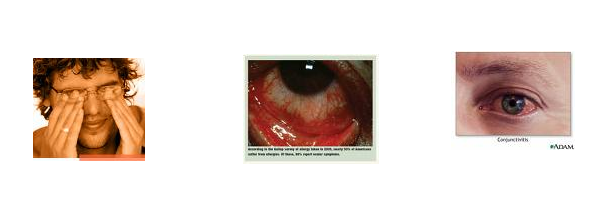
- Allergic conjunctivitis
- Vernal conjunctivitis
- Giant papillary conjunctivitis
- Allergic conjunctivitis = It is a type hypersensitivity allergic reaction characterized by itching which is the hallmark.
Symptoms either symptoms include
- tearing
- Burning
- Sinus pressure behind the eye or ears.
Symptoms :- The various features of an examination include.
- Swelling of lids.
- Dilatation of conjuctival nessalls.
- Discharge in acute reaction.
- Pallor of palpebral conjuctiva.
- Absence of giant papillae.
- Corneal dillen due to excessive earms of allergic conjuctivities.
- Mild to moderate
- Severe and prolonged.
Pathegenesis = studies suggest that cell mediated immune response also contributes in the pathogenesis of allergic conjuctivities. There is an increased infiltration of the activated fibroblasts and langerhan cells expressing HLA- DR antigen.
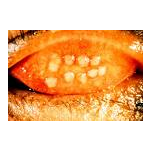
DIAGNOSIS :- A comprehensive history distinet physical fendings and adjunct diagnostics tests make the diagnosis simple. A differential diagnosis from bacterial conjunctivitis is important.
Tests for differential diagnosis
- Pose Bengal staining.
- Tear meniscus.
- Schemers test.
- Bleak up time evaluation
- Type of mucous
- Conjunctional sera ping
- Tear cytology
- Positive ocular challenge to allergen.
Other methods in the predictions of allergic reactions are
- Allergy skin testing - INVITRO PAST
- Use of phaddiatop pediatrics management of Allergic conjunctivitis.
A ) Prevention
B ) Therapentic
- Pharmacotherapy
- Immunotherapy
A ) Prevention = Removal of offending allergen.
- Mast cell stabilizers
- Cromolyn sodium
- Ladoxamide 1%
- Ketotifen
- Loteprednal etabonate of (0.5% ophthalmic suspension.
- H1 antagonists
- Systemic
- Local
- Steroids
- Short acting
- Intermediate acting
- Long acting.
- NSAIDS ( Kato loc )
- Ganglioside derivatives
- Immuno-modulators
- Immunotherapy.
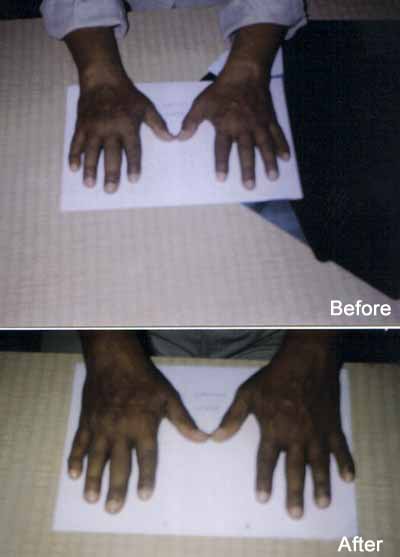
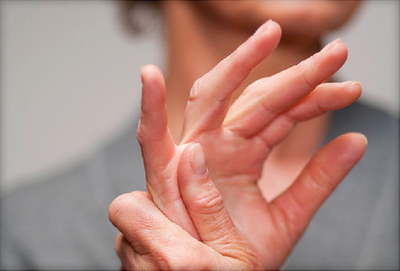
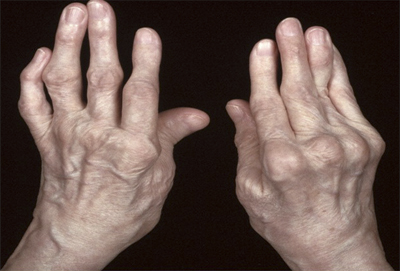
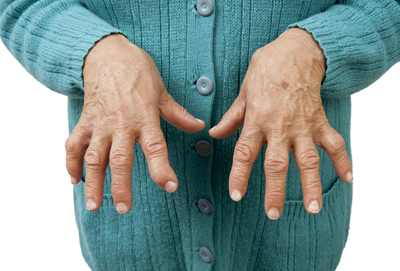
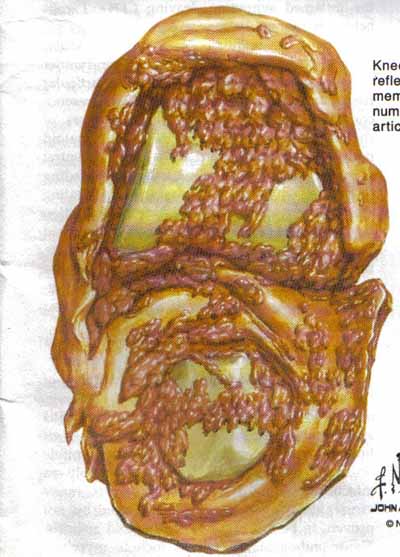
Rheumatoid Arthritis (संधीवात) :
Amongst all joint diseases Rheumatoid Arthritis is very common disorder. This is more common in elderly women and
Essentials of diagnosis
- Insidious onset, bilateral symmetrical small joint involvement, progression ids untripetal, deformities common ( Swan neck, boutonnieres )
- Prodromal symptoms of malaise, fever, weight loss, morning stiffness.
- X –ray shows extra articular osteoporosis, joint erosions, narrowing of joint spaces.
- Extra articular manifestations subcutaneous modules, pleuro- pericarditis, lymphadenopathy splenomegaly with leucopenia and vasculities ( sclerities and aortitis )
- Rheumatoid factor usually positive ( IgM against IgG )
Treatment:
- Physical rest
- Occupational therapy
- Systematic and articular rest.
- Muscular straight endurance.
- NSAID ( particularly COXZ inhibitors ) valdecoxib, etorrcoxib.
- Disease modifying agents; Gold, penicillin.
- TNF inhibitor- infliximab
- Corticosteroids
- Methotrixate
- Sulfasalazaline
- Leflunoinide.
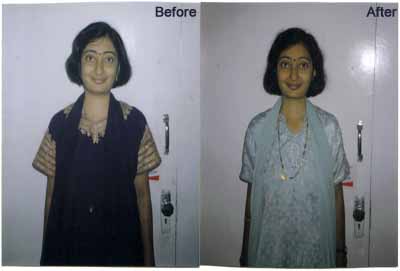
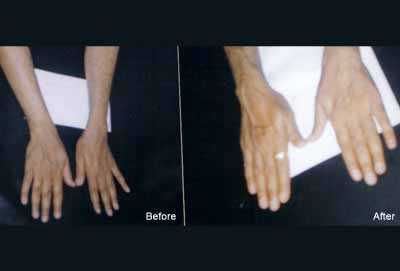

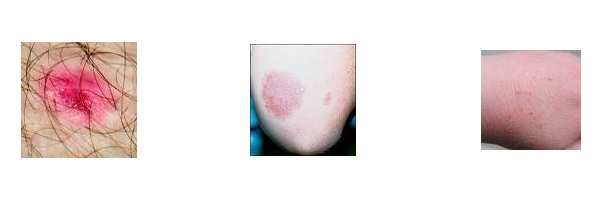
Atopic Dermatitis :
It is a Type I reactions. Defined as a chronically relapsing skin disease that usually manifests for the first time in childhood . This disease is a complex interplay of several environmental, food, behavioral and immunological factors in genetically predisposed individuals. It is commonly associated with frequent episodes of sore throat , running nose and asthma It is more common is urban than rural areas . Skin lesions are associated with intense itching, worsening in cold and dry weather. Lesions usually begin with red rashes over the cheeks, fore head and scrap; slowly spreading to the trunk and outer aspect of extremit Siapeu area is typecrtky speed in children with increasing age . lesious end is occur in skin folds / fleseurs , face and neck . Atopic Dermatitis improues of goes into remission near pubuty explaining the conditions and natural history of the disease to the patients / parents of children and there proper councelling foms the cornerstone of management . Expert of the skin to irrelant chemical and physical treatment should be avoided . Among the plethora of treatment options, tpical corticostirocds , emotions and oral sedetine anti histrminics remain the means try of treatment . Their judicious use ofter proper selection of the patient is minatory .
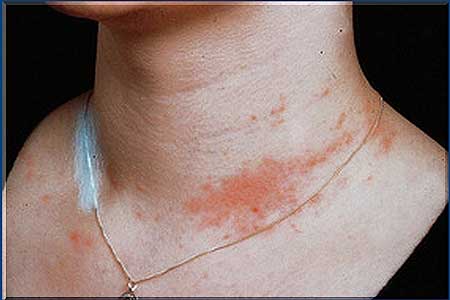
Urticaria :
Urticaria is cheracterised by raised erythematous skin lesious that are markedly puritic , generally . cuoesening on scratching . The basic pathomechanism includes activation of mast cells by figger factor leading to viberations of mediators , cousing nesodilation and sesoluting is shelling of the tissue . Lesions and secondary to physical figger , pressure vibration stimulus , change in temperature , following exercise , sun-incpsure , food intake and contact with centre . A detailed history forms the ministry of diagnosis , supported by urraous skin tests , the including open patch test , prick test , the scratch test , the scratch test , the scratch chamber test , the tissue test . Advice and informations on should be provided . Cooling lotions like calamine help in returning pruiritis , besides oral antihistomics . Oral cortieosteloids may surmetines be required in shout tepering couese .
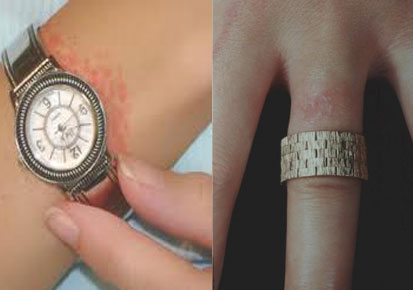
Allergic Contact Dermatitis :
It is an acquired sensitivity to various substances that produce inflamantory.
Immunotherapy / Hyposensitization/ Allergy shots :
To reduce the sensitivity of body to allergens a prolonged course of serial injections is given to allergy patients. It’s called immunotherapy or hyposensitization. It is also described as allergy shots by patients.
It can be ascending dose of injections or oral sublingual tablets (SLIT) or drops
Allergic rhinitis, or hay fever and asthma is most commonly treated disease with this form of therapy.
Please Note- The course , doses, durations and allergens are all to be decided by allergy specialists
- All the allergens are to be preserved in refrigerator.
- Each time the dose will be decided by the physician.
- Injection if given can be in skin or just below. i.e. intradermal or subcutaneous.
- Patient should stay under observation for twenty minutes.
- In case of allergic there will be intense itching of injection site, increased swelling, more generalized spread of skin swelling , angio neurotic oedma,
- In case of severe reaction fall in blood pressure, shock has been noted.
- Therefore prompt treatment has to be instituted.
- Please keep the record ready each time for doctor’s reference.



